Calculated Fields
Contents
Introduction
A calculated field is calculated from other fields in the list. The calculated field itself does not exist in the data source. Its value for each row is calculated from the values of the other fields.
The calculated value does not have to be numeric. In fact you can calculate a date, a time duration, or perform some text manipulation to create the value.
Adding a Calculated Field
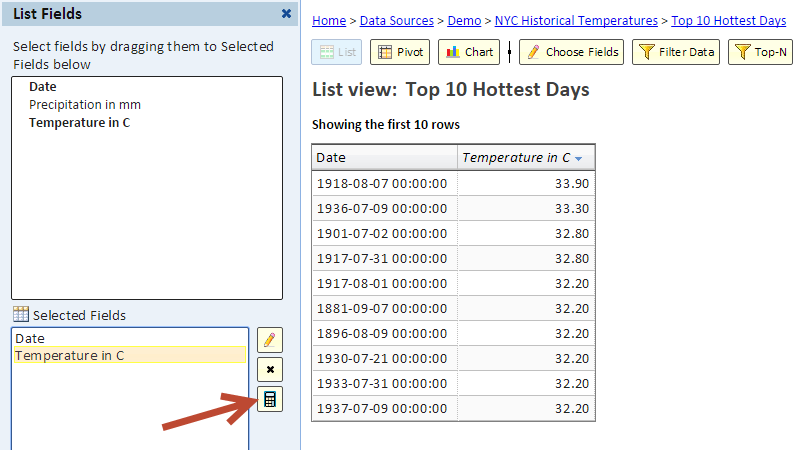
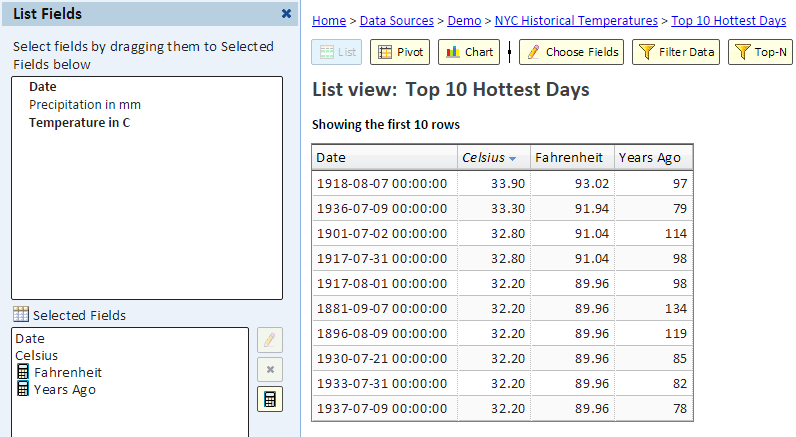
To see how to add a calculated field, let's see an example. We'll start with this view showing the 10 hottest days in NYC. The temperatures are shown in Celsius.
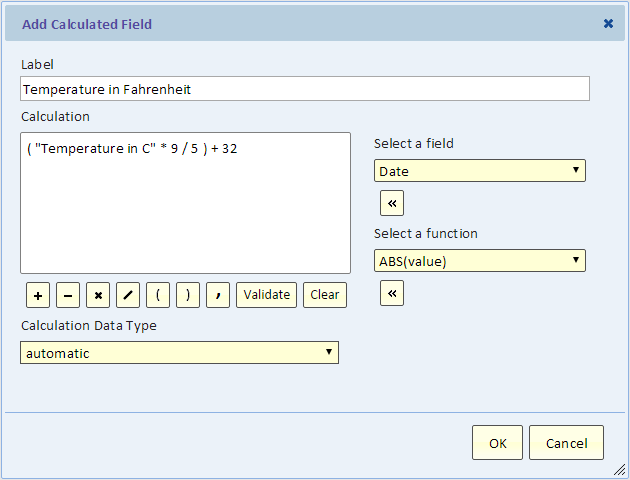
To also show the temperatures in Fahrenheit, we'll add a calculated field by clicking the calculator button (see arrow in the above picture).
Using the Calculated Field dialog, we can build a calculation that can include arithmetic as well as a selection of functions. For this example, we only need arithmetic.
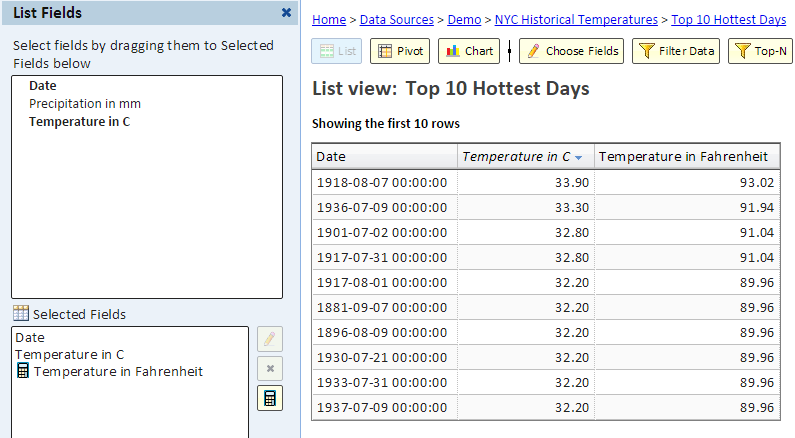
The following picture shows the list view with the calculated field:
Adding a Function to the Calculation
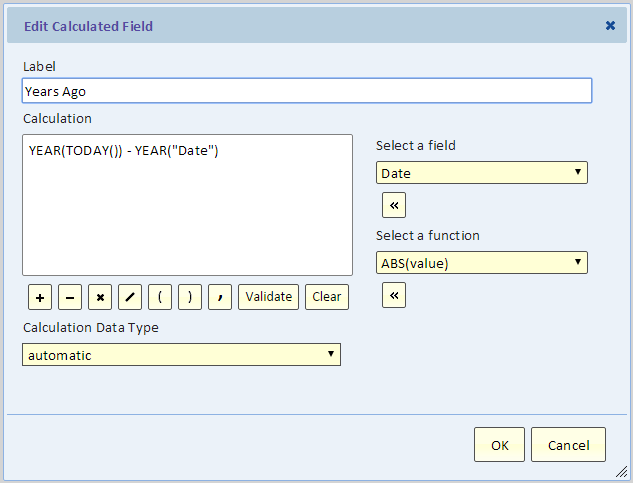
To demonstrate the use of functions in a calculation, let's continue with our example, and calculate the number of years ago when we saw that temperature.
The calculation extract the year part of the date and subtract it from the year part of today's date. The TODAY() function returns today's date. The YEAR() function returns the year part of the date as a number.
Next is the list view with the "Years Ago" field.
Functions
The table below shows all the functions that are available for field calculations.
- ABS(value) - Absolute value. The value must be numeric and the returned value is based on the type of the value.
- DURATION(begin,end) - Difference in seconds between the begin and end. The returned value is of type duration.
- NOW() - The current date and time (at the data source of this list view).
- TODAY() - The current date. Same as NOW, but with the time part truncated.
- DATE_ADD(date,duration) - adds the duration (number of seconds) to the date and returns the new date
- DATE_ADD(date,interval,count) - adds count intervals to the date. Count is the number of intervals and the interval can be YEAR, QUARTER, MONTH, WEEK, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, or SECOND
- DATE_SUB(date,duration) - subtract the duration (number of seconds) from the date and returns the new date
- DATE_SUB(date,interval,count) - subtracts count intervals from the date. Count is the number of intervals and the interval can be YEAR, QUARTER, MONTH, WEEK, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, or SECOND
- YEAR(date) - the year part of a datetime value returned as a number (e.g. 2015)
- QUARTER(date) - the quarter of the year - a number between 1 and 4
- MONTH(date) - the month of the year - a number between 1 and 12
- DAY(date) - the day of the month - a number between 1 and 31
- HOUR(date) - the hour of the day - a number between 0 and 23
- MINUTE(date) - the minute of the hour - a number between 0 and 59
- SECOND(date) - the second - a number between 0 and 59
- REPLACE(text,item,replacement) - Replaces all occurrences of text item with replacement. The result is text
- TRUNC(value) - if value is numeric, the fraction part is removed. If value is datetime, the time-of-day part is removed
- TRUNC(date,interval) - truncate the date down to the specified interval. For example, if interval is YEAR, the result is the top of the year (January 1 at 00:00:00). Similarly, QUARTER is top of the quarter, MONTH is top of month, WEEK_MONDAY is the start time of the week (Monday), WEEK_SUNDAY is the beginning of the week (Sunday), DAY is the date without the time part, HOUR is the date and time truncated to the beginning of the hour
- ROUND(value) - rounds a numeric value to an integer
- FORMAT(value,format) - if value is date/time, the format will be a date/time format. The format is specified according to the Java format. For example, 'MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm' would render: 12/06/2014 17:46. If value is numeric, the format will be a number format.
- TO_DATE(text) -
- CONCAT(text,text,...) -
- SEARCH(text,item,found,not found) -
- CSV_SEARCH(csv,item,found,not found) -
- CSV_SELECT(csv,n) -
- IFNULL(value,replacement) -
FORMAT date format, decimal format using Java simple date format and decimal format (like we do in Global Settings custom format and in Scorecard Item custom format) varchar TO_DATE cast a varchar date or datetime into datetime expects ISO date but will also take mm/dd/yyyy datetime CONCAT concatenate two or more texts CONCAT(text1, text2) CONCAT(text1, text2, text3,…) varchar SEARCH Search the text for item1. If found, return item 2, otherwise return item3 SEARCH(text, item1, item2, item3) varchar CSV_SEARCH Search a comma-separate text for item1. If found, return item2, otherwise item3 CSV_SEARCH(text, item1, item2, item3) varchar CSV_SELECT Select the nth item in a comma-separated text. Items are numbered from 1 (first) If the text has less than n items, return null CSV_SELECT(text, n) varchar IFNULL If the input is null or empty, replace it with a new value. The type of value must agree with the type of text IFNULL(input, value) based on the type of input